Running Sum of Purchases
Picture a daily ledger that tracks every purchase made at a small market. Each number in the list represents the value of a purchase as it was recorded throughout the day. Your task is to calculate the running total after each entry, forming a new list that captures how the sum grows with every transaction. This running sum offers an immediate snapshot of how earnings accumulate and helps the owner understand their progress moment by moment.
Think of the array as a line of customers, each adding their contribution to the cash register. The first customer creates the baseline, the next builds upon it, and the process continues until the day ends. By the time you reach the last number, the running sum should tell you the total revenue. The challenge is to traverse the list, gather the previous totals, and include the current value to update the cumulative tally at each step.
If the list is empty, there are no transactions, so return an empty list. When values are negative, they represent refunds or discounts that reduce the total, yet they still appear in the running sum. Begin with a clean slate, proceed through the array, and produce a parallel list where each position reflects the balance immediately after that purchase was processed.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,3,6,10]
Explanation: The running totals after each purchase are 1, 3, 6, and 10.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Explanation: Each purchase adds 1, so the running sum increments steadily.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
Output: [3,4,6,16,17]
Explanation: The cumulative totals reflect how each purchase increases the balance.
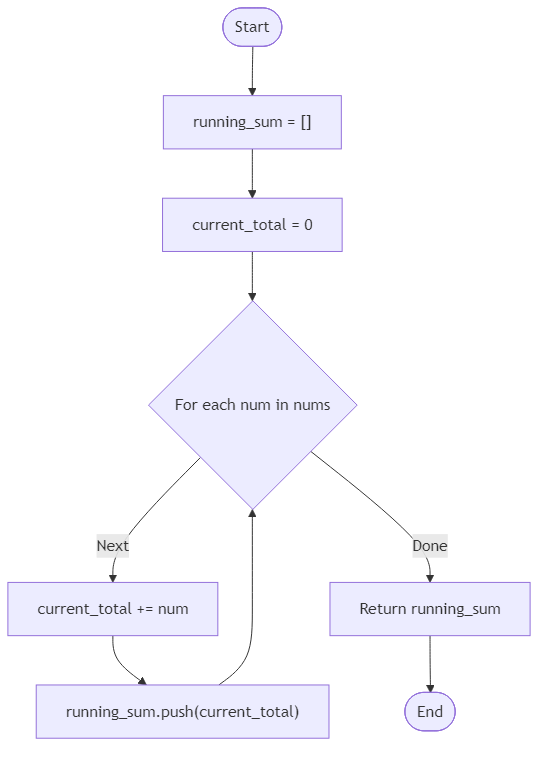
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public Object running_sum(Object nums) {
int[] arr = (int[]) nums;
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>(); int t = 0;
for (int n : arr) { t += n; r.add(t); }
return r;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
