Longest Consecutive Sequence
You are given an unsorted array of integers nums. Your task is to find the length of the longest consecutive sequence of elements. A consecutive sequence is a sequence of numbers where each number appears exactly one more than the previous one (for example, 1, 2, 3, 4). The numbers do not need to be adjacent in the array but must form a continuous range.
Imagine a collection of scattered puzzle pieces, each labeled with a number. Your goal is to assemble the longest chain of consecutive numbers. For instance, if you have [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2], the longest chain you can form is [1, 2, 3, 4], giving a length of 4. The array might contain duplicates or gaps, but your answer must represent the largest possible continuous block of numbers.
This problem teaches you about using sets or maps to efficiently detect sequences and avoid unnecessary sorting or nested loops. It demonstrates how to identify continuity within unordered data by recognizing patterns of connected numbers.
If there are no elements, return 0. If there is only one element, return 1.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1]
Output: 9
Example 3:
Input: nums = []
Output: 0
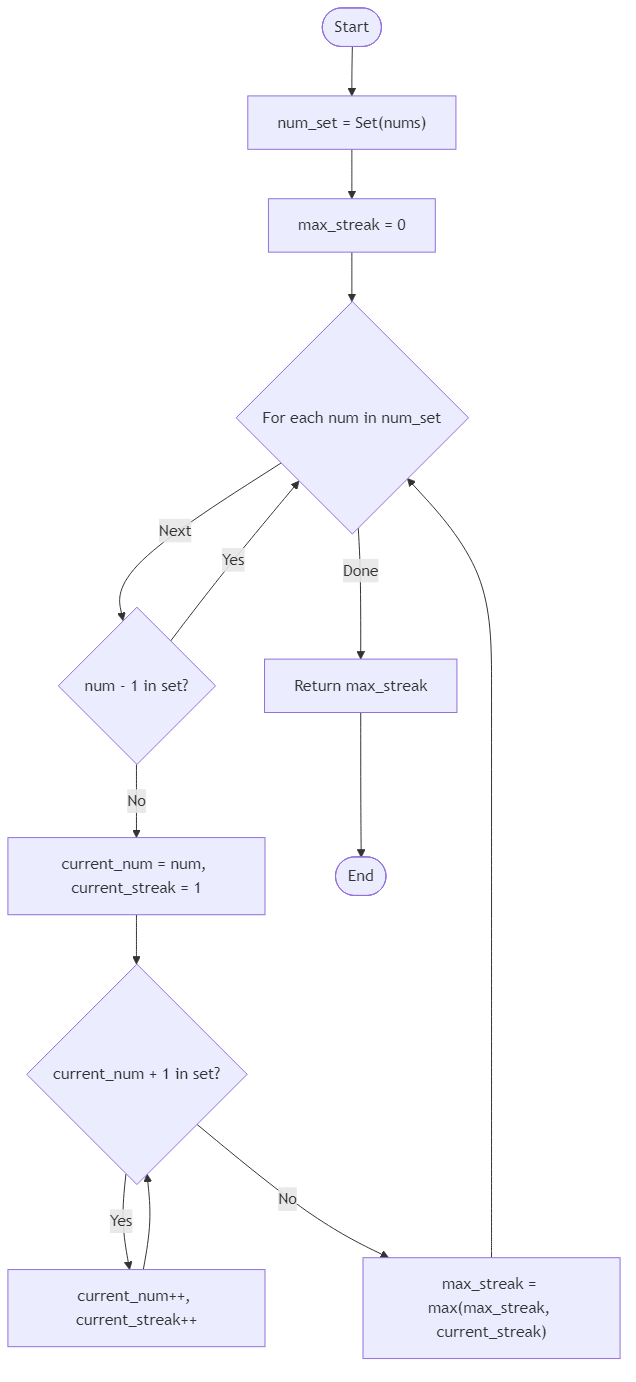
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int longest_consecutive(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int x : nums) set.add(x);
int maxLen = 0;
for (int x : set) {
if (!set.contains(x - 1)) {
int current = x, streak = 1;
while (set.contains(current + 1)) {
current++; streak++;
}
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, streak);
}
}
return maxLen;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
