Running Sum of 1D Array
You are given an array of integers. Your task is to return an array that represents the running sum of the input. The running sum at a given index is defined as the sum of all elements from the start of the array up to that index, inclusive. This means that for every position in the resulting array, the value is the total of all numbers encountered so far.
Imagine keeping track of your savings day by day. Each day, you add today’s savings to your previous total, giving you a cumulative amount. Similarly, in this problem, each position in the array builds on the previous one, growing as it moves forward. This concept is commonly used in financial tracking, cumulative scores, and progressive computations.
If the array is empty, return an empty array. If there is only one element, the result is the same as the input. The running sum must preserve the order of the original numbers.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,3,6,10]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
Output: [3,4,6,16,17]
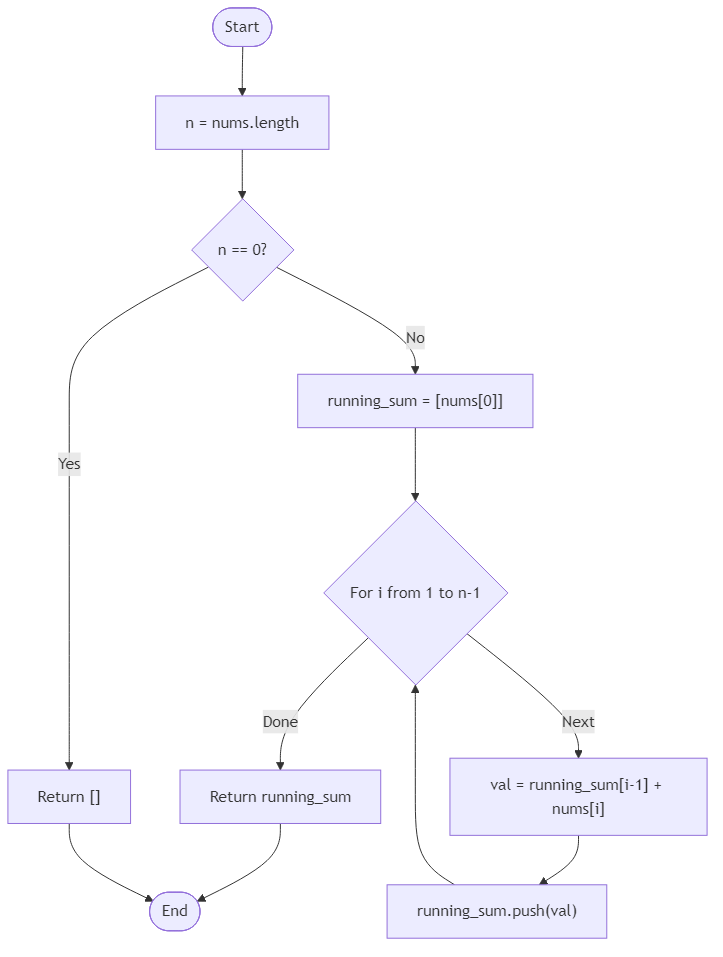
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public Object running_sum(Object nums) {
int[] arr = (int[]) nums;
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int total = 0;
for (int num : arr) {
total += num;
result.add(total);
}
return result;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
