Moonlit Orchid Bloom
At the Crescent Conservatory, gardeners celebrate each lunar crest with the Moonlit Orchid Bloom. The ceremony begins with a single orchid unfurling at the center of a glass basin. A caretaker announces how many bloom rings will follow, and the guides place one fresh orchid at the rim of each new ring. Mirrors suspended in the greenhouse then reflect every blossom from the prior ring twice, creating a soft halo that wraps the courtyard in pale light.
The horticulturists insist on precision because each reflection helps pollinators navigate after dusk. Once the rim orchid opens, every earlier bloom glows again in mirrored pairs, and observers carefully record the count in leather-bound ledgers. The routine never shifts: add one guiding blossom, then echo the previous ring twice without fail.
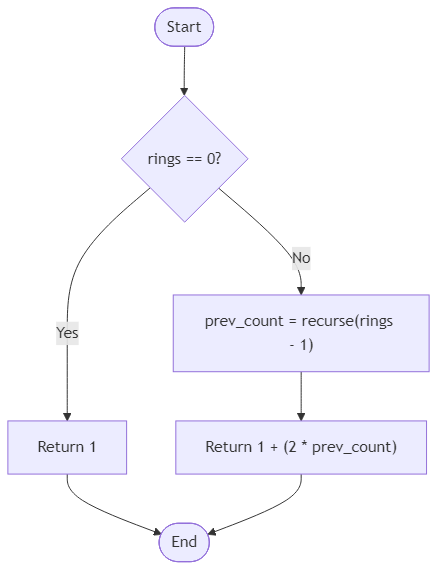
Your goal is to determine how many blooms are visible when the final ring settles. The input, rings, is a non-negative integer. When rings equals zero, only the central orchid shines. For any higher value, add one new blossom for the ring and double the complete display from the previous ring. Return the total number of visible blossoms as an integer.
Example 1:
Input: rings = 0
Output: 1
Explanation: Only the central orchid opens.
Example 2:
Input: rings = 2
Output: 7
Explanation: The second ring adds one blossom and reflects the earlier blooms twice.
Example 3:
Input: rings = 5
Output: 63
Explanation: Five rings follow the pattern, yielding sixty-three glowing orchids.
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
class Solution {
public int calculate_orchid_height(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = i + dp[(i-2)];
}
return dp[n];
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
