Maximum Product Subarray
You are given an integer array nums. Your task is to find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) that has the largest product and return that product. The subarray must be a sequence of consecutive elements within the array, not necessarily unique, and its length can vary from 1 to the entire array.
Unlike sum-related problems, this task requires considering both positive and negative values because multiplying by a negative number can invert the outcome. For example, two negative numbers can create a larger positive product, while zeros can interrupt the sequence and reset progress. Handling such dynamic changes makes this problem an interesting challenge in reasoning about subarray boundaries and maintaining multiple states as you traverse the array.
This problem illustrates the importance of tracking both the maximum and minimum products up to each point, since a large negative product might turn into a large positive product later. It’s widely used to understand optimization under multiplicative relationships.
If the array has only one element, that element itself is the maximum product. Zeros may appear anywhere and should be treated as separators between subarrays.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,-2,4]
Output: 6
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-2,0,-1]
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: nums = [-2,3,-4]
Output: 24
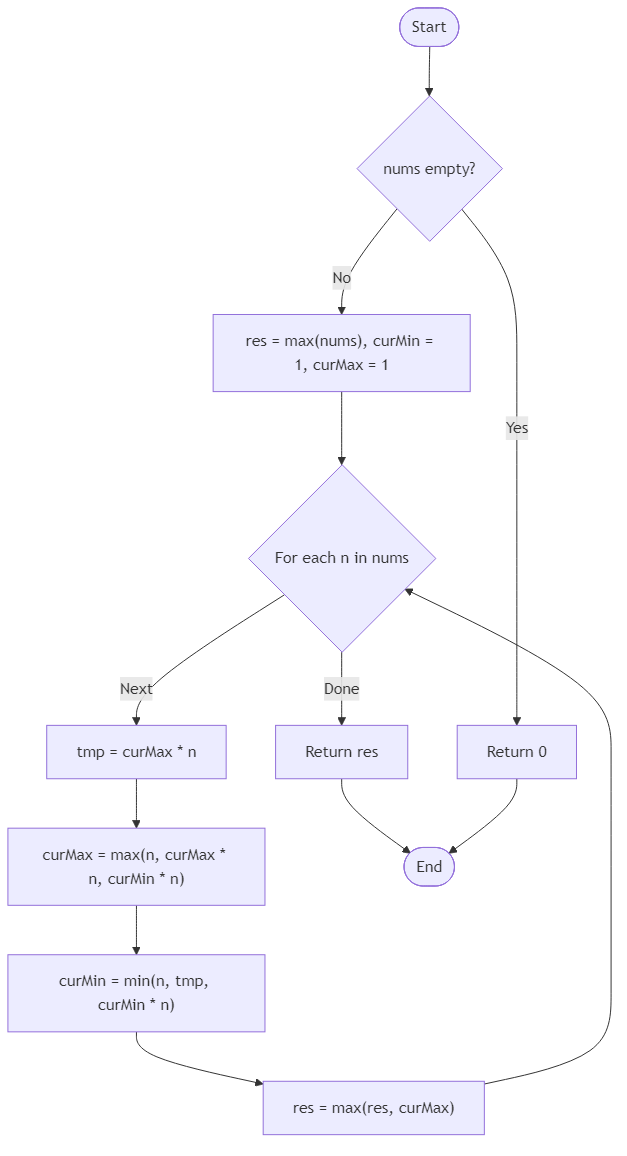
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
class Solution {
public int max_product(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
int res = nums[0], maxP = nums[0], minP = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
int x = nums[i];
if (x < 0) {
int tmp = maxP; maxP = minP; minP = tmp;
}
maxP = Math.max(x, maxP * x);
minP = Math.min(x, minP * x);
res = Math.max(res, maxP);
}
return res;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
