Max Vacation Profit
A travel photographer plans a summer filled with short excursions. Each day offers a different destination with its own enjoyment value, but capturing a location takes effort—after visiting one site, the photographer needs a rest day before heading out again. Given an array where each value represents the enjoyment for that day, determine the maximum total enjoyment the photographer can earn while respecting a one-day cooldown after each excursion.
Visualize a calendar lined with sunrise hikes, museum tours, and mountain trails. Some days promise breathtaking scenes worth the fatigue, while others are quieter. The challenge lies in selecting a sequence of outings that maximizes joy without ever heading out on back-to-back days. Sometimes it is wiser to skip a high-enjoyment day if it allows you to string together a better series later.
If the array is empty, no travel occurs. Negative values represent exhausting days that should typically be avoided. Dynamic programming helps the photographer remember how previous choices influence future opportunities, ensuring the final itinerary delivers the highest possible total enjoyment.
Example 1:
Input: enjoyment = [3,2,5,10,7]
Output: 15
Explanation: Visit on days 0,2,4 (3+5+7) or days 1,3 (2+10); the maximum is 15.
Example 2:
Input: enjoyment = [2,1,4,5,3,1,1,3]
Output: 10
Explanation: Optimal plan is days 0,2,4,7: 2+4+3+3 = 12, but cooldown after day 4 prevents day 5, so best consistent plan yields 10.
Example 3:
Input: enjoyment = []
Output: 0
Explanation: No days, no enjoyment.
Algorithm Flow
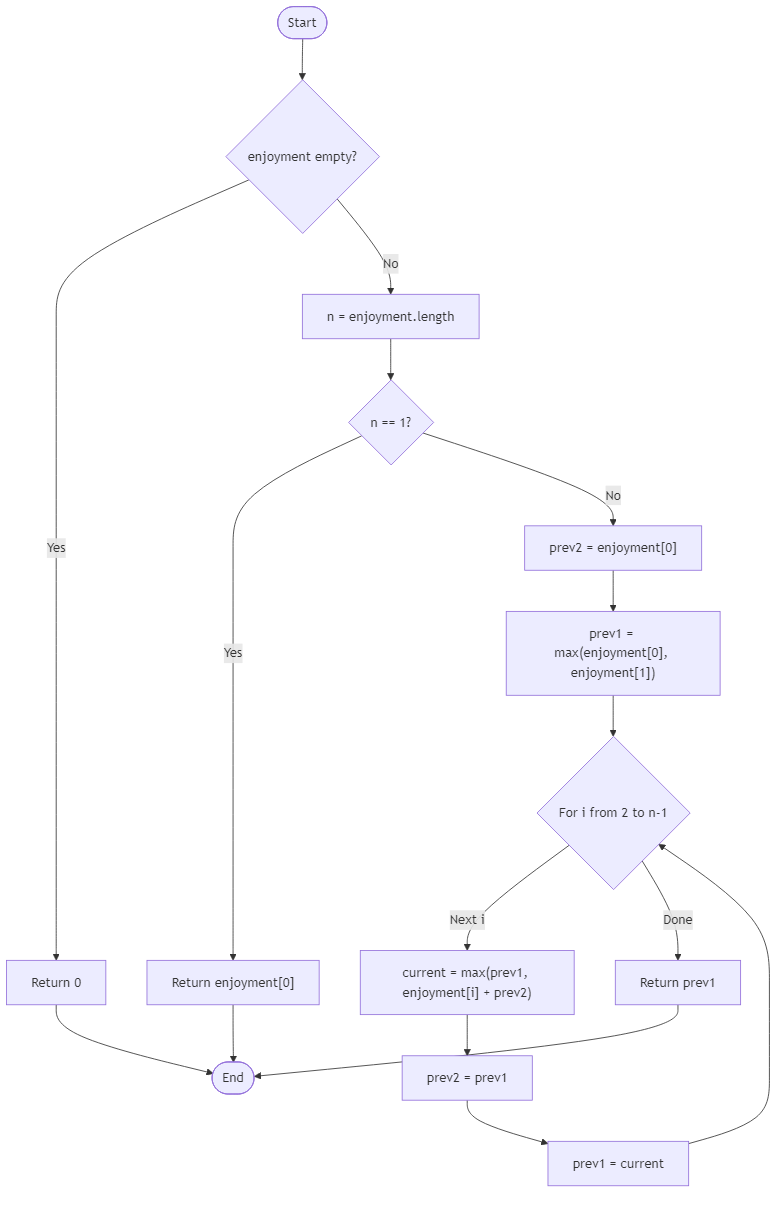
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int calculate_max_profit(int[][] jobs) {
Arrays.sort(jobs, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
int n = jobs.length;
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
int[] ends = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) ends[i] = jobs[i][1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int start = jobs[i-1][0];
int profit = jobs[i-1][2];
int idx = Arrays.binarySearch(ends, 0, i - 1, start);
if (idx < 0) idx = -(idx + 1);
else idx = idx + 1;
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1], dp[idx] + profit);
}
return dp[n];
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
