Max Harvest with Rest
On a hillside farm, each plot yields a certain number of energy-rich fruits. The farmer can choose to collect crops from one plot per day, but after harvesting a particular plot, they must rest the following day to tend the soil and prevent exhaustion. You are given an array where each element represents the harvest value for a plot in chronological order. The goal is to compute the maximum total harvest the farmer can collect while respecting the mandatory rest day between harvests.
Visualize the harvest plan as a line of sunlit terraces. Some terraces gleam with a heavy yield, while others offer only a modest return. The farmer wants to chart a schedule that captures as much fruit as possible without ever working on two consecutive days. This scheduling challenge rewards careful choices: sometimes it is best to skip a high-yield day if doing so unlocks even greater opportunities later on.
If the array is empty, the farmer earns nothing. Negative values represent plots that would drain energy (perhaps due to pests or poor weather) and should generally be avoided unless they enable access to better plots ahead. The optimal solution relies on balancing immediate reward with future potential, making dynamic programming the ideal guiding strategy.
Example 1:
Input: harvest = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Harvest plots at indices 0 and 2 for a total of 4.
Example 2:
Input: harvest = [2,7,9,3,1]
Output: 12
Explanation: Harvest plots at indices 1, 3, and 4 (7+3+1) or indices 0,2,4 (2+9+1); the maximum is 12.
Example 3:
Input: harvest = []
Output: 0
Explanation: No plots mean no harvest.
Algorithm Flow
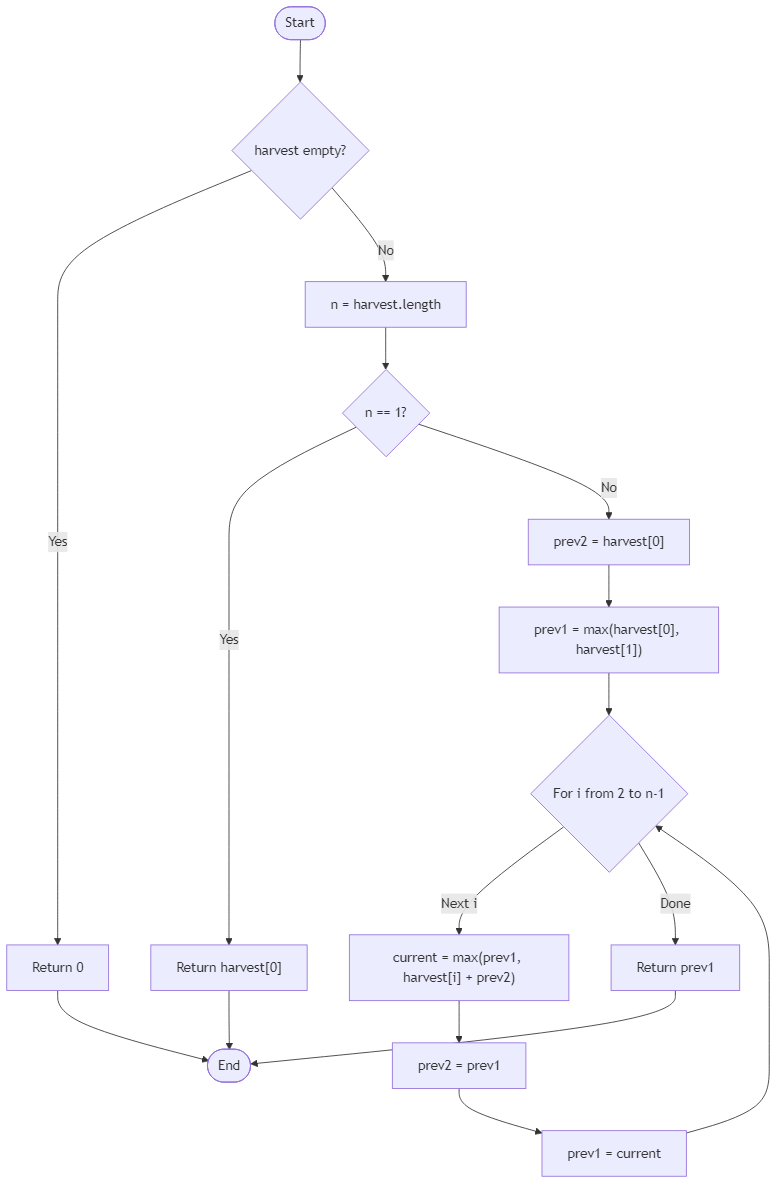
Best Answers
class Solution {
public int max_harvest_with_rest(Object harvest) {
if (harvest == null) return 0;
int[] h = (int[]) harvest;
if (h.length == 0) return 0;
if (h.length == 1) return Math.max(0, h[0]);
int prev2 = Math.max(0, h[0]);
int prev1 = Math.max(prev2, h[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < h.length; i++) {
int current = Math.max(prev1, Math.max(0, h[i]) + prev2);
prev2 = prev1;
prev1 = current;
}
return prev1;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
