Last Value Not Exceeding Target
You are given a list of integers arranged in ascending order and a target value. Your task is to identify the position of the last element in the list that does not exceed the target. In other words, among all values that are less than or equal to the target, you must find the one that appears furthest to the right and return its index. If the list is empty, or if all elements are greater than the target, the correct answer is -1.
Think of the numbers as markers placed along a timeline that increases from left to right. Starting from the beginning, every value that remains at or below the target is acceptable, but you are interested in the final such marker before values begin to surpass it. This position represents the boundary where the sequence transitions from numbers that satisfy the condition to numbers that do not. Duplicates may appear, and when multiple items are equal to the target, the desired position is the index of the last occurrence among them.
The result is an integer index within the list. If the target is smaller than the first element, there is no qualifying position and the answer is -1. If the target is at least as large as the greatest element, then the answer is the final index of the list. Focus on the notion of ordered placement and boundary identification, and return the single index that best represents the last value not exceeding the target.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 4, 4, 7], target = 4
Output: 3
Explanation: The last value not exceeding 4 is the second 4 at index 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3, 5, 6], target = 2
Output: -1
Explanation: All elements are greater than 2, so no valid index exists.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2, 3, 3, 3, 9], target = 10
Output: 4
Explanation: The target is at least the largest element, so the last index is 4.
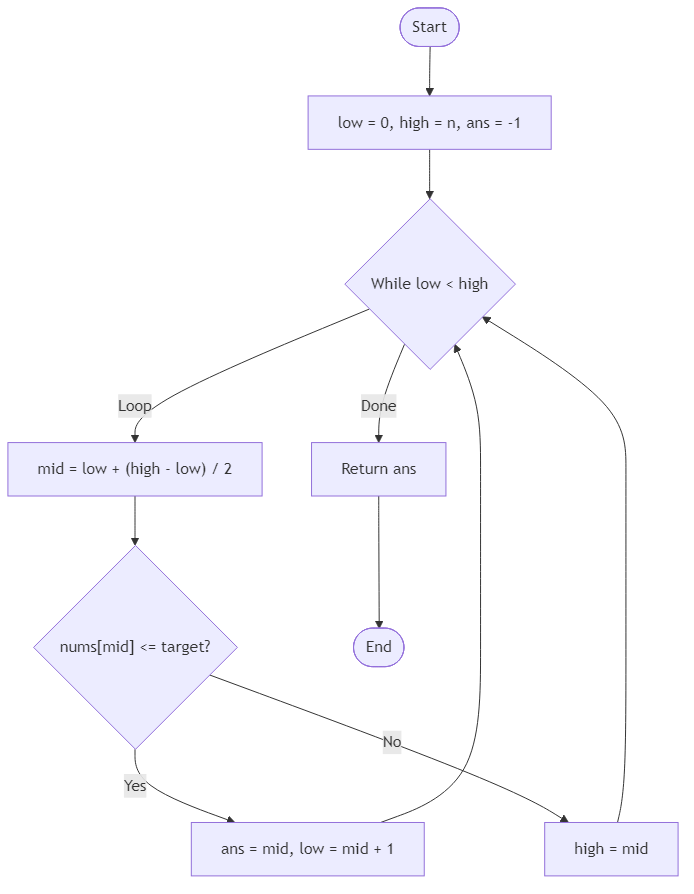
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
class Solution {
public int find_last_not_exceeding(Object nums, Object target) {
int[] arr = (int[]) nums;
int t = (int) target;
int result = -1;
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] <= t) {
result = mid;
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return result;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
