Harbor Banner Schedule Slots
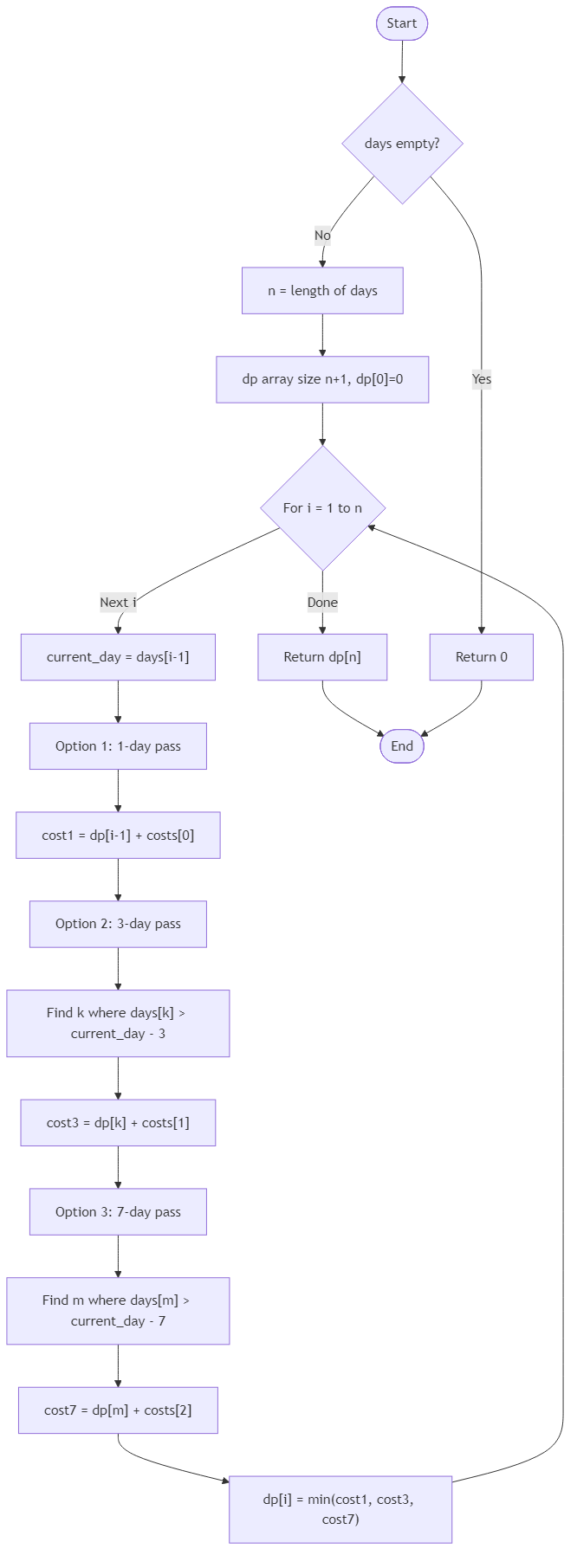
The harbor promenade assigns banner crews to specific nights when visiting ships dock, and the schedule repeats throughout the month. Instead of hiring crews night by night, the coordinator can purchase passes that cover consecutive evenings: a 1-night pass for targeted work, a 3-night pass for short runs, or a 7-night pass when celebrations span an entire week. Given the exact nights that require coverage, the team wants the minimum total cost to ensure every listed night is staffed, with passes allowed to overlap and extend beyond the final night if necessary.
Your routine receives a strictly increasing array of positive integers representing the nights in the month that demand banners, along with an array of three integers giving the cost of 1-, 3-, and 7-night passes. Use dynamic programming to decide which combination of passes yields the lowest price while covering all required nights; the input arrays must remain unchanged. Single-night schedules should simply compare the three options, and an empty schedule yields cost zero. This budget check lets the harbor confirm crew reservations, reserve equipment carts, and promise visiting captains that their arrivals will be celebrated without overspending.
Example 1:
Input: days = [1,4,6,7,8,20], costs = [2,7,15]
Output: 11
Explanation: Buy 1-day passes for nights 1,4,6 and a 7-day pass covering 7,8,20.
Example 2:
Input: days = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], costs = [3,8,20]
Output: 9
Explanation: Three 3-day passes cover the entire week for cost 9.
Example 3:
Input: days = [], costs = [5,10,20]
Output: 0
Explanation: No scheduled nights mean no passes are needed.
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int calculate_min_slots(int[][] intervals) {
int[] starts = new int[intervals.length];
int[] ends = new int[intervals.length];
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
starts[i] = intervals[i][0];
ends[i] = intervals[i][1];
}
Arrays.sort(starts);
Arrays.sort(ends);
int slots = 0, pEnd = 0;
for (int s : starts) {
if (s < ends[pEnd]) slots++;
else pEnd++;
}
return slots;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
