Aurora Feather Lights
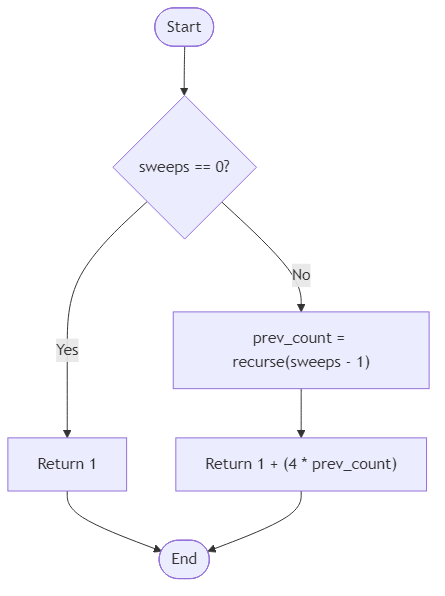
The technical objective is to calculate the total number of illuminated feathers in a cascading aurora display after a specified number of geometric sweeps. Each sweep follows a recursive growth pattern where one new guiding feather is added, and the entire previous display is replicated fourfold through mirrored paths.
The final output must be an integer representing the total feather count according to the recurrence $f(n) = 1 + 4 imes f(n-1)$, with the base case $f(0) = 1$ (the initial guiding feather). The solution must handle non-negative integer inputs efficiently, modeling the exponential growth of the display as the number of sweeps increases. This provides a precise quantitative measure for timing caravans and monitoring sky lane safety in Borealis Strait.
Example 1:
Input: sweeps = 0
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: sweeps = 2
Output: 21
Example 3:
Input: sweeps = 4
Output: 341
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[][] find_maximal_balanced_subarrays(int[] nums) {
int p0 = 0, p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
Map<String, List<Integer>> diffs = new HashMap<>();
diffs.computeIfAbsent("0,0", k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int r = (nums[i] % 3 + 3) % 3;
if (r == 0) p0++;
else if (r == 1) p1++;
else p2++;
String key = (p0 - p1) + "," + (p1 - p2);
diffs.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(i);
}
List<int[]> balanced = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> indices : diffs.values()) {
for (int a = 0; a < indices.size(); a++) {
for (int b = a + 1; b < indices.size(); b++) {
balanced.add(new int[]{indices.get(a) + 1, indices.get(b)});
}
}
}
List<int[]> maximal = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] b1 : balanced) {
boolean isSub = false;
for (int[] b2 : balanced) {
if (b2[0] <= b1[0] && b2[1] >= b1[1] && (b2[0] != b1[0] || b2[1] != b1[1])) {
isSub = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isSub) maximal.add(b1);
}
maximal.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[][] result = new int[maximal.size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < maximal.size(); i++) {
int start = maximal.get(i)[0];
int end = maximal.get(i)[1];
result[i] = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, start, end + 1);
}
return result;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
