Balanced Mod Subarrays
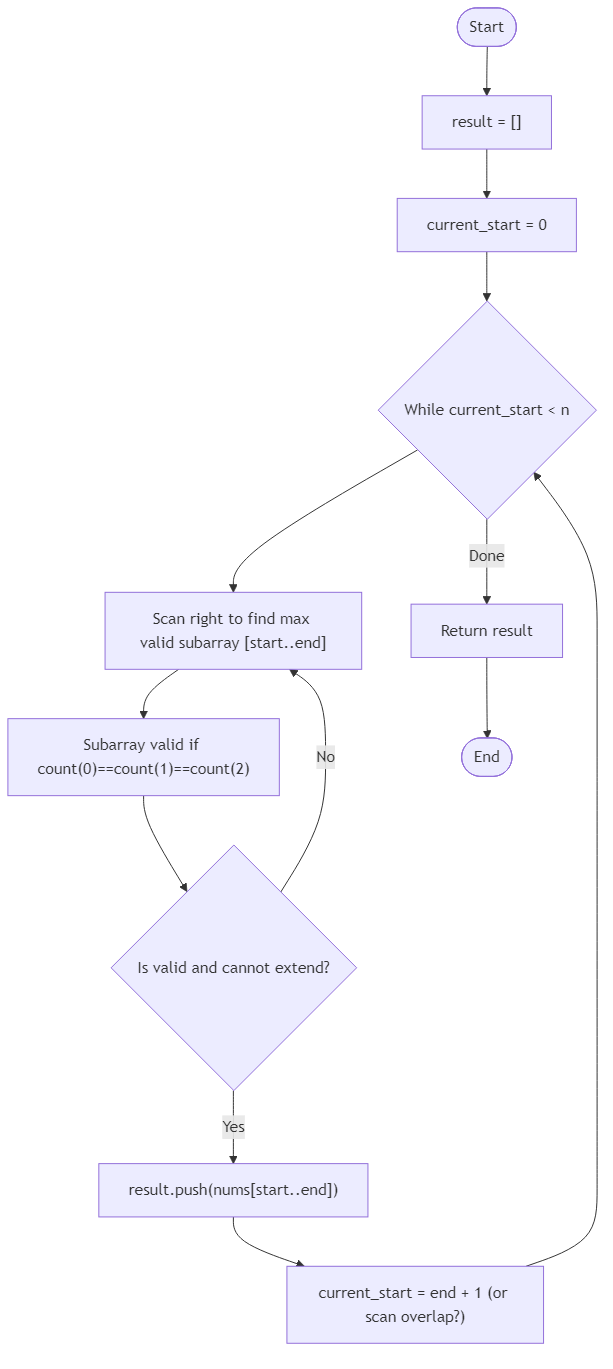
The technical objective is to identify all inclusion-maximal contiguous subarrays where elements with remainders 0, 1, and 2 (modulo 3) appear in equal frequency. A balanced subarray is considered maximal if it is not a proper subsegment of any other balanced subarray within the dataset.
The final output must be a collection of these maximal segments, returned in their original order of occurrence. The solution must handle negative integers by calculating their correct modulo 3 remainders and efficiently filter the entire sequence to find valid balanced regions. This ensures that researchers can accurately track and analyze periods of perfect calibration, exploration, and stabilization within the observed event timeline.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Output: [[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1, 4, 7, 10]
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3, 6, 9, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7, 12, 15, 18]
Output: [[3, 6, 9, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7], [6, 9, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7, 12], [9, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7, 12, 15], [2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7, 12, 15, 18]]
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[][] find_maximal_balanced_subarrays(int[] nums) {
int p0 = 0, p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
Map<String, List<Integer>> diffs = new HashMap<>();
diffs.computeIfAbsent("0,0", k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int r = (nums[i] % 3 + 3) % 3;
if (r == 0) p0++;
else if (r == 1) p1++;
else p2++;
String key = (p0 - p1) + "," + (p1 - p2);
diffs.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(i);
}
List<int[]> balanced = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> indices : diffs.values()) {
for (int a = 0; a < indices.size(); a++) {
for (int b = a + 1; b < indices.size(); b++) {
balanced.add(new int[]{indices.get(a) + 1, indices.get(b)});
}
}
}
List<int[]> maximal = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] b1 : balanced) {
boolean isSub = false;
for (int[] b2 : balanced) {
if (b2[0] <= b1[0] && b2[1] >= b1[1] && (b2[0] != b1[0] || b2[1] != b1[1])) {
isSub = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isSub) maximal.add(b1);
}
maximal.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[][] result = new int[maximal.size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < maximal.size(); i++) {
int start = maximal.get(i)[0];
int end = maximal.get(i)[1];
result[i] = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, start, end + 1);
}
return result;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
