Wildlife Bridge Network Scan
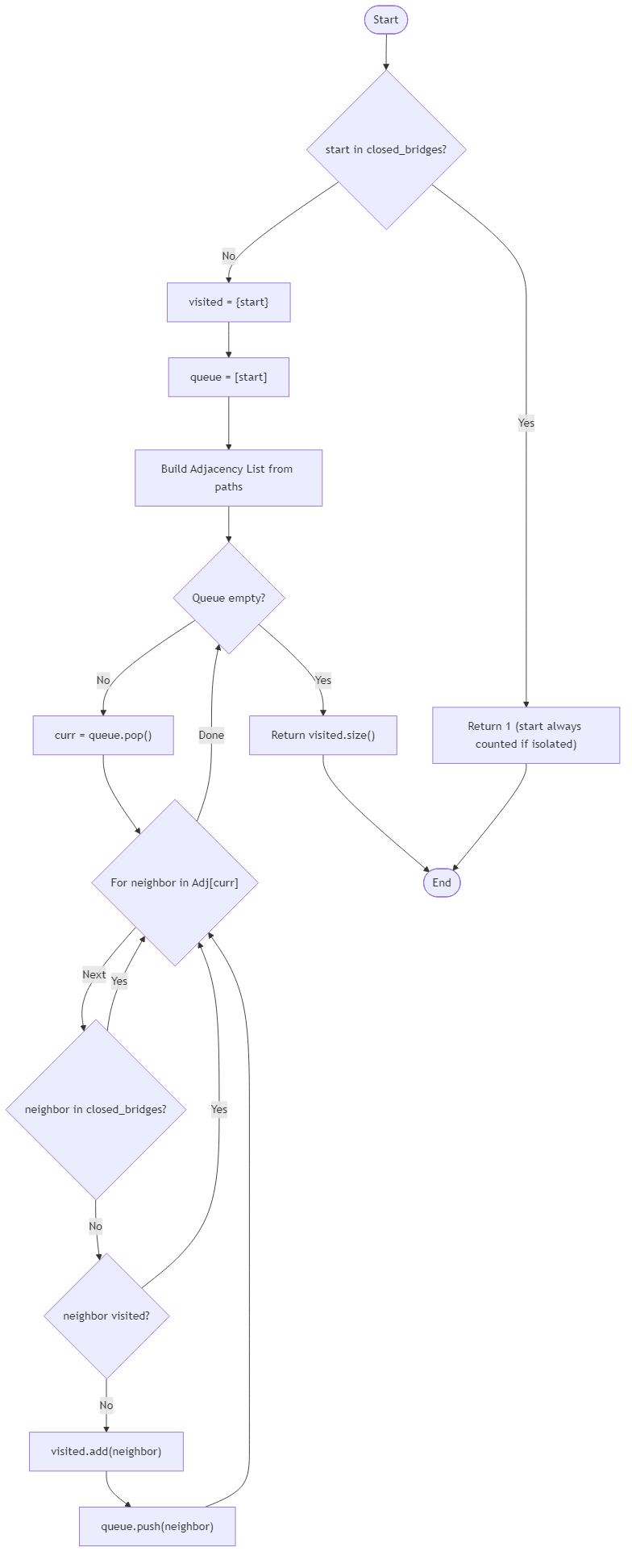
The objective is to quantify the extent of a reachable network within an undirected graph of $n$ nodes, given a specific starting point and a set of restricted nodes. This task requires determining the size of the connected component that originates from the start node while traversing only through those bridges not identified as closed_bridges.
The final output must be an integer representing the total count of distinct, accessible open bridges, including the starting location. The solution must handle various graph topologies, redundant path entries, and scenarios where restricted nodes effectively partition the network or isolate the starting point. This ensures an accurate census of the traversable infrastructure under specific seasonal conditions.
Example 1:
Input: n = 6, paths = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[2,5]], start = 0, closed_bridges = [4]
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, paths = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]], start = 2, closed_bridges = [1,3]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, paths = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]], start = 4, closed_bridges = []
Output: 4
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int wildlife_bridge_reach(int n, int[][] paths, int start, int[] closed_bridges) {
List<List<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
Set<Integer> closed = new HashSet<>();
for (int b : closed_bridges) closed.add(b);
for (int[] path : paths) {
if (path[0] < n && path[1] < n) {
adj.get(path[0]).add(path[1]);
adj.get(path[1]).add(path[0]);
}
}
if (closed.contains(start)) return 0;
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited.add(start);
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curr = queue.poll();
for (int neighbor : adj.get(curr)) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbor) && !closed.contains(neighbor)) {
visited.add(neighbor);
queue.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
return visited.size();
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
