Mountain Cabin Signal Range
The alpine rescue service oversees a string of mountain cabins connected by narrow suspension bridges spanning deep valleys. Each cabin is numbered from 0 to n - 1, and the dispatch team maintains a map of every two-way bridge that allows teams to cross between cabins. After a heavy snowfall, certain bridges become unsafe, and the teams must avoid those crossings while transmitting readiness signals from a particular base cabin. The rescue coordinator wants to know how many cabins will actually receive the signal without stepping onto the blocked bridges.
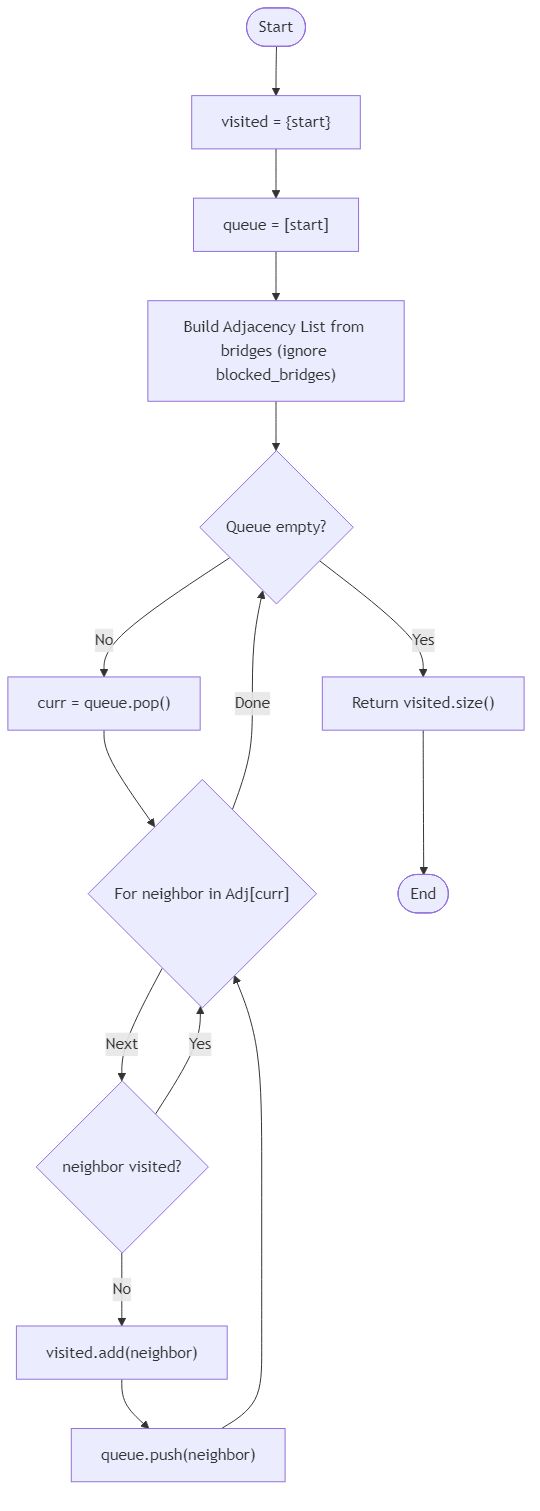
Write a function that takes the cabin count n, the list of bridges bridges, the starting cabin start, and a set blocked_bridges storing every bridge segment that is currently closed. Each bridge is represented by [u, v], and the blocked set lists the same format. The bridge data may include duplicates or reversed entries, which should not affect the final reachability count. Rescue teams may traverse any open bridge in either direction and count each cabin at most once. If the starting cabin is isolated or every adjacent bridge is blocked, only the origin receives the signal.
Return the number of cabins that hear the signal, including the starting cabin when it has at least one open path to itself. Ignore bridges that appear in blocked_bridges, and treat duplicates as a single connection. Provide the result as an integer with no additional formatting.
Example 1:
Input: n = 6, bridges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]], start = 0, blocked_bridges = [[2,3]]
Output: 3
Explanation: Cabins 0, 1, and 2 receive the alert before reaching the blocked bridge between cabins 2 and 3.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, bridges = [[0,2],[2,1],[1,3],[3,4]], start = 2, blocked_bridges = []
Output: 5
Explanation: With no blocked bridges, the signal reaches every cabin in the connected component.
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, bridges = [[0,1],[1,2]], start = 3, blocked_bridges = [[2,1]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Cabin 3 stands alone, so only the origin is counted.
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
class Solution {
public double calculate_min_range(int[][] cabins) {
int n = cabins.length;
if (n <= 1) return 0.0;
double[] minD = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(minD, Double.MAX_VALUE);
minD[0] = 0.0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
double res = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && (u == -1 || minD[j] < minD[u])) u = j;
}
visited[u] = true;
res = Math.max(res, minD[u]);
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!visited[v]) {
double d = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(cabins[u][0] - cabins[v][0], 2) + Math.pow(cabins[u][1] - cabins[v][1], 2));
minD[v] = Math.min(minD[v], d);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
