Merge Sorted Arrays
You are given two sorted arrays of integers. Your goal is to merge them into a single array that is also sorted in non-decreasing order. The merged array should contain all elements from both input arrays. This operation should be performed in such a way that the relative ordering of equal elements remains consistent with their original arrays.
Imagine combining two already organized lists—such as two playlists sorted by time or two ranked lists of scores—into one seamless ordered list. You must ensure no element is lost or duplicated beyond what exists in the inputs. The key challenge lies in efficiently combining both lists while maintaining sorted order and minimizing unnecessary operations.
The resulting merged list should include all values from both arrays, and if one of them is empty, the result should simply be the other array. The final result must be sorted, even when negative numbers or repeated values are present.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3], nums2 = [2,5,6]
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1], nums2 = []
Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [], nums2 = [2,3]
Output: [2,3]
Algorithm Flow
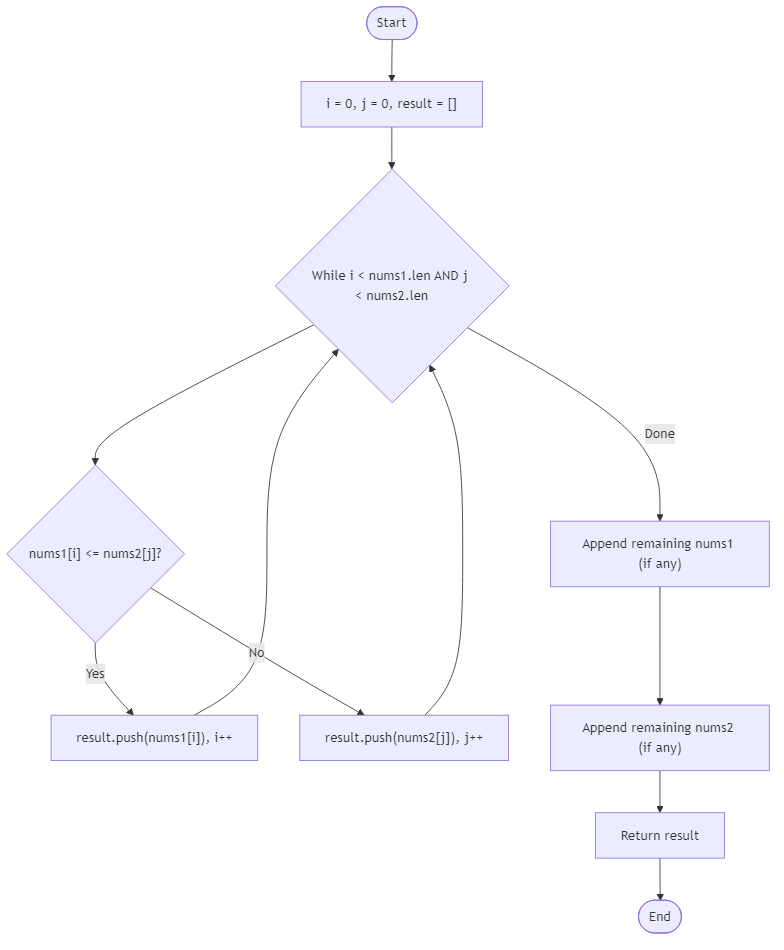
Best Answers
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public Object merge(Object nums1, Object nums2) {
int[] arr1 = (int[]) nums1;
int[] arr2 = (int[]) nums2;
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) {
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
result.add(arr1[i]);
i++;
} else {
result.add(arr2[j]);
j++;
}
}
while (i < arr1.length) {
result.add(arr1[i]);
i++;
}
while (j < arr2.length) {
result.add(arr2[j]);
j++;
}
return result;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
