Handle Nullable Values Safely
Learn Java Optional to write null-safe code that eliminates NullPointerException risks. You will work with Optional containers to represent values that may or may not be present, using methods like map, flatMap, filter, and orElse to transform and extract values safely.
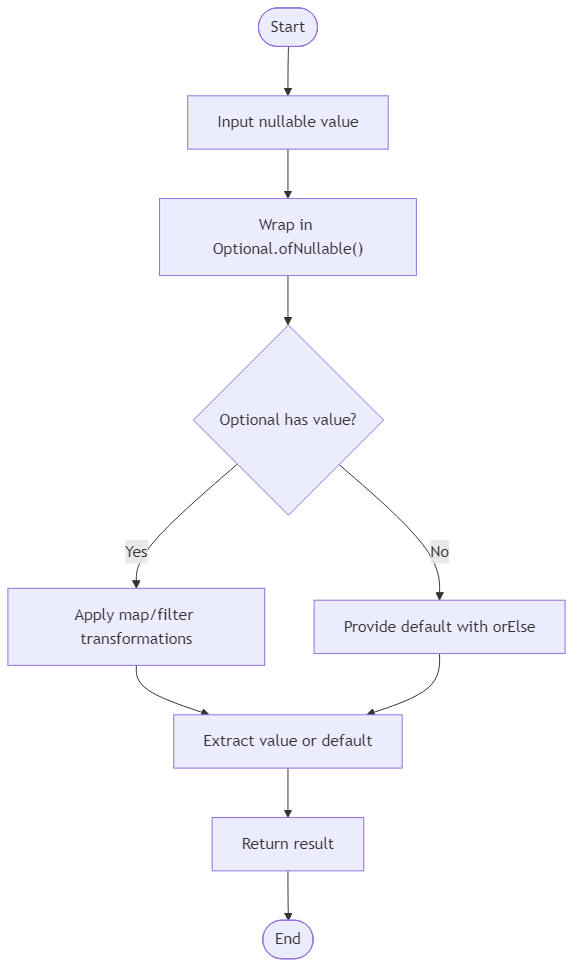
Your task is to refactor code that traditionally uses null checks into elegant Optional chains. This modern approach makes your code more readable and forces explicit handling of absent values.
Example 1:
Input: value = "hello"
Output: "HELLO"
Explanation: Transform present value to uppercase.
Example 2:
Input: value = null
Output: "default"
Explanation: Return default value when Optional is empty.
Example 3:
Input: numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Output: Optional[3]
Explanation: Find first odd number greater than 2.
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.Optional;
class Solution {
public String processValue(String value) {
Optional<String> opt = Optional.ofNullable(value);
return opt.filter(v -> !v.isEmpty()).orElse("Guest");
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
