Festival Booth Priority Sort
The city's autumn festival schedules dozens of pop-up booths, each with a numeric priority that determines how close vendors stand to the main stage. During setup, coordinators receive a stream of late-arriving merchants along with the exact index where each booth should slot into the current lineup. After all arrivals insert themselves, staff must confirm the final order to ensure crowd-control signs point to the correct locations.
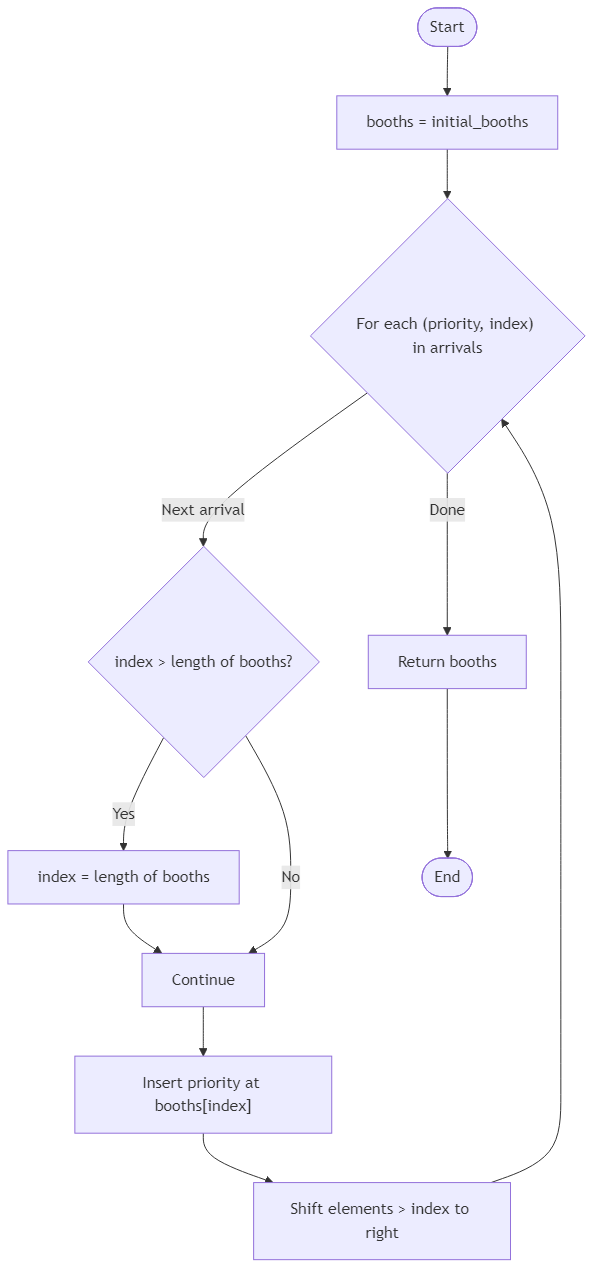
You will receive an initial list booths of priorities ordered from lowest to highest, and a list arrivals of [priority, index]. Process arrivals sequentially: insert each priority into booths at position index (0-based), shifting later booths to the right. If index equals the length of the current list, append the booth to the end. Return the final ordered list once all arrivals are placed.
The insertions keep booths sorted by priority only if coordinators choose correct indices, so your simulation should not reorder values beyond the instructed insert position.
Example 1:
Input: booths = [10,20,40], arrivals = [[30,2],[15,1]]
Output: [10,15,20,30,40]
Explanation: Insert priority 30 at index 2 to get [10,20,30,40], then insert 15 at index 1.
Example 2:
Input: booths = [5,7], arrivals = [[6,1],[8,3]]
Output: [5,6,7,8]
Explanation: Insert 6 between 5 and 7, then append 8.
Example 3:
Input: booths = [12], arrivals = []
Output: [12]
Explanation: No new booths arrive, so the lineup stays unchanged.
Algorithm Flow
Best Answers
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] sort_priorities(int[] nums) {
int[] res = nums.clone();
Arrays.sort(res);
return res;
}
}Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
