City Bus Loop Access
Technical Goal
Implement a function to determine the number of distinct stops reachable from a starting origin in a circular bus system, where certain stops are closed and cannot be visited or traversed. The system is represented as an undirected graph.
Constraints
n: Total number of stops (0 to n-1).roads: A list of two-way connections[u, v].start: The origin stop index.closed_stations: A list of indices representing unreachable stops.
Rules
- If
startis inclosed_stations, return 0. - A path is only valid if all stops on the path (including
startand the target stop) are not inclosed_stations. - Return the total count of unique accessible stops reachable via open roads.
Example 1:
Input: n = 6, roads = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]], start = 0, closed_stations = [3] Output: 3 Explanation: The bus visits stops 0, 1, and 2 before encountering the closed stop at 3.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, roads = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2],[2,3],[3,4]], start = 2, closed_stations = [4] Output: 4 Explanation: Stop 4 is closed, but the remaining stops 0, 1, 2, and 3 remain connected.
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, roads = [[0,1],[1,2]], start = 3, closed_stations = [] Output: 1 Explanation: Stop 3 has no connecting roads, so the bus stays at its origin.
Algorithm Flow
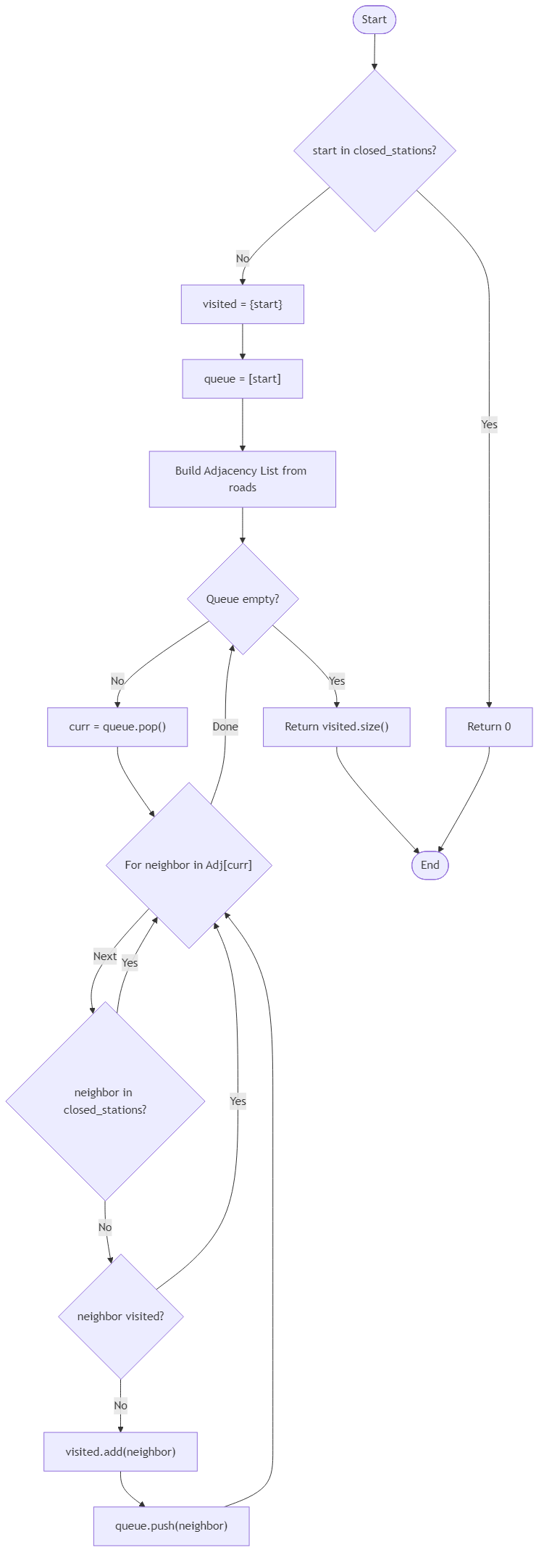
Recommendation Algorithm Flow for City Bus Loop Access - Budibadu
Best Answers
java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int city_bus_loop_access(int n, int[][] roads, int start, int[] closed_stations) {
Set<Integer> closed = new HashSet<>();
for (int s : closed_stations) closed.add(s);
if (closed.contains(start)) return 0;
List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] road : roads) {
adj[road[0]].add(road[1]);
adj[road[1]].add(road[0]);
}
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited.add(start);
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (!visited.contains(v) && !closed.contains(v)) {
visited.add(v);
queue.add(v);
}
}
}
return visited.size();
}
}Related Tree Problems
Comments (0)
Join the Discussion
Share your thoughts, ask questions, or help others with this problem.
